In a world where data breaches and cyber attacks make headlines daily, you might think Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is enough. However, cyber threats are evolving. Enter Three-Factor Authentication (3FA), an enhanced security protocol that adds an extra layer of protection, making unauthorized access even more difficult. This comprehensive guide explores what 3FA is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.
The Foundations of 3FA
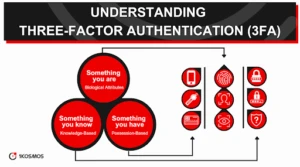
What is 3FA?
Three-Factor Authentication (3FA) is a security protocol that adds an extra layer of protection on top of traditional Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). 3FA requires users to present three identifying factors before accessing an account, app, or system.
This typically involves something the user knows (password), something the user has (a mobile phone or security device), and something the user is (biometric data).
The concept behind 3FA is straightforward: the more authentication factors involved, the harder it is for unauthorized users to gain access. It's a comprehensive approach to security that makes the verification process more robust by reducing the chances of a breach.
The Evolution from 2FA to 3FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) has been the industry standard for securing accounts and systems. However, as cyber threats grow in sophistication, there is an increasing need for more rigorous security measures.
3FA evolved as a response to this need, incorporating an additional layer of security beyond 2FA, making it even more difficult for unauthorized users to access accounts.
This third layer could be a fingerprint scan, iris recognition, voice verification, or behavioral pattern analysis. It depends on the system and its security requirements. By adding this additional layer, 3FA significantly raises the bar for attackers trying to compromise a system.
Who Needs to Know About 3FA?
3FA is increasingly relevant to a broad audience. Organizations dealing with sensitive or classified information are the most obvious candidates for 3FA.
This includes government agencies, healthcare institutions, and financial firms. However, any organization looking to bolster its cybersecurity posture can benefit from implementing 3FA.
Individual users with heightened security needs, such as public figures or high-profile business professionals, can also benefit from 3FA. As awareness of cyber threats grows, even the general public is beginning to appreciate more advanced security protocols.
How Does 3FA Work?
The mechanics of 3FA are a natural extension of 2FA, with the addition of a third factor for validation. Like 2FA, the user must provide two forms of identification plus a third, distinct type of identity-confirming credentials.
The 3FA Process Explained
Typically, 3FA starts with the user entering a username and password. Next, a secondary device, like a smartphone, receives a time-sensitive code.
After entering this code, the user must provide a third form of identification: a fingerprint or retina scan, voice recognition, or some other form of biometric verification. Only after successfully passing through all three gates does the user gain access to the system or account.
Types of Factors in 3FA
The factors used in 3FA typically fall into three categories: knowledge-based (something you know), possession-based (something you have), and inherence-based (something you are).
Knowledge-Based Factors: Include passwords and PINs.
Possession-Based Factors: Encompass mobile devices, hardware tokens, or smart cards.
Inherence-Based Factors: Refer to biometrics like fingerprints, iris scans, or facial recognition.
Different combinations of these categories can be employed depending on the level of security required. It's important to note that the three factors should be distinct to maximize security benefits.
3FA Protocols and Mechanisms
Several protocols and mechanisms support the implementation of 3FA. These range from standard protocols like OAuth and OpenID to specialized options for high-security environments.
Additionally, hardware tokens and biometric scanners might be integrated into the system for the third factor.
The appropriate protocol and mechanism selection depends on various factors, including the organization's existing infrastructure, user needs, and specific security requirements.
Benefits of 3FA
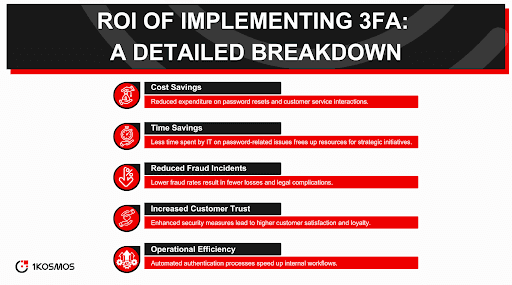
3FA offers many advantages, making it a worthy investment for organizations seeking robust security solutions. It dramatically reduces the chances of unauthorized access and aligns well with various regulatory standards.
Improved Security Posture
The most significant benefit of 3FA is its enhanced security. By requiring three distinct verification forms before accessing accounts, 3FA makes it exponentially more challenging for unauthorized users to gain access. This is particularly beneficial for organizations handling sensitive data where the stakes for identity theft are high.
Regulatory Compliance
Another advantage of 3FA is its alignment with various regulatory standards. For organizations that must comply with guidelines such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, implementing 3FA can aid in achieving and maintaining compliance. It is a tangible demonstration of an organization's commitment to safeguarding user data.
User Experience and Usability
While adding more steps to the login process might seem like a burden, many modern 3FA solutions are designed with user experience in mind. Biometric authentication, for instance, can be quicker and more natural to provide than entering a complex password. As a result, the additional security layer does not necessarily come at the expense of usability.
Implementing 3FA
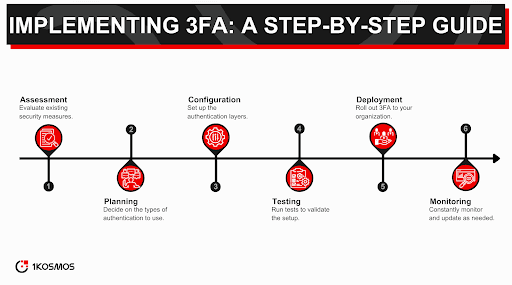
Technical Requirements
Implementing 3FA requires some technological adjustments. At a minimum, organizations must ensure they have the infrastructure to support this security measure. This could include software that supports multi-factor authentication protocols and hardware like biometric scanners or token generators.
A secure and reliable network is also essential for 3FA to function optimally. While cloud-based solutions are available, organizations must maintain strong network security protocols to minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Costs and Budgeting
The implementation of 3FA involves both upfront and ongoing costs. Upfront costs may include the purchase of hardware and software and the expenses related to system integration. Ongoing costs can encompass maintenance, updates, and possibly licensing fees.
Budgeting for 3FA should consider not only the direct costs but also the potential savings from reduced security incidents. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term benefits often justify the expenditure.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While 3FA offers enhanced security, poor implementation can undermine its effectiveness. One common pitfall is inadequate staff training, leading to user errors that compromise security. Proper training and awareness programs can mitigate this risk.
Another issue is over-reliance on one type of authentication factor, such as using multiple biometric identifiers, which defeats the purpose of multi-factor authentication. A diversified approach using various types of authentication factors is recommended.
Potential Challenges and Criticisms
The Complexity Issue
One criticism of 3FA is the added complexity it introduces. Critics argue that while the system is more secure, it becomes more cumbersome. However, many 3FA solutions focus on improving the user experience to mitigate this issue, and the benefits of heightened security often outweigh the downsides.
Reliance on Technology
Another concern is the heavy reliance on technology, such as smartphones or biometric devices, which could malfunction or be lost. This reliance creates a potential weak link in the security chain. To counter this, backup options and alternative authentication methods should be part of any comprehensive 3FA strategy.
User Acceptance and Training
As with any new system, user acceptance is often a hurdle. People generally resist change, particularly when it comes to technology that requires them to alter their habits. Effective training and awareness programs can go a long way in facilitating smooth adoption.
Emerging Trends in 3FA
As the digital landscape evolves, so does 3FA. One emerging trend is the integration of artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the authentication process. Machine learning algorithms could, for example, analyze user behavior to provide a more dynamic and secure form of authentication.
Beyond facial recognition, fingerprints, and iris scans, new forms of biometric data, such as heart rate or brainwave patterns, are being explored.
Blockchain technology has also been touted as a possible element in the future of 3FA. It offers the potential for decentralized authentication methods that are not only secure but also more user-friendly. The immutable nature of blockchain records can further enhance the security aspects of 3FA.
Conclusion
3FA offers a heightened level of security that is becoming increasingly essential in our digitalized world. The potential applications and benefits are vast, from government agencies to everyday internet users. While implementing 3FA involves a range of logistical and technological considerations, the upside in terms of cybersecurity makes it a worthy investment.
If you're committed to taking your organization's digital security to the next level, contact our team today to learn more about implementing 3FA.





