The 1Kosmos Architectural Advantage
Why BlockID
Reusable Identity Wallet
Portability and Interoperability
Verifiable Claims / Credentials
Key Benefits
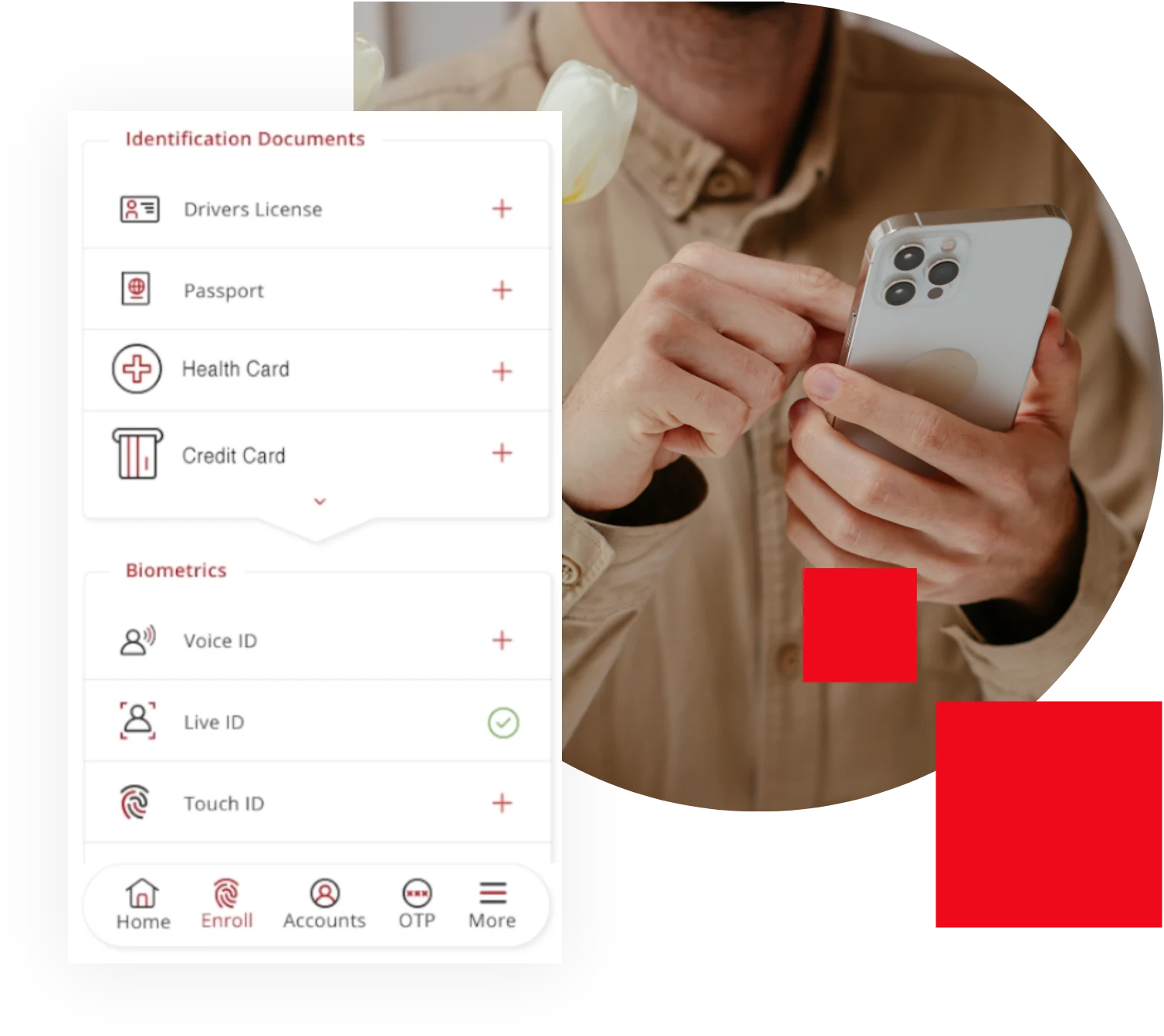
Remote User Onboarding
The 1Kosmos digital wallet organizes and stores information gathered, triangulated and validated during the identity proofing stage of remote user onboarding. This includes attributes from multiple, proof-able sources and enables a wide variety of applications that verify the identity without requiring them to physically meet in person, for example, worker and contractor onboarding, resident applications for government services, and know your customer identity verification for financial services. All personal information is encrypted end-to-end and then becomes readily available anywhere at any time upon user consent. Virtually any combination of government issued credentials (eg, driver’s license, passport), banking records, telco providers, and employment records can be used and subsequently stored securely in the digital wallet.
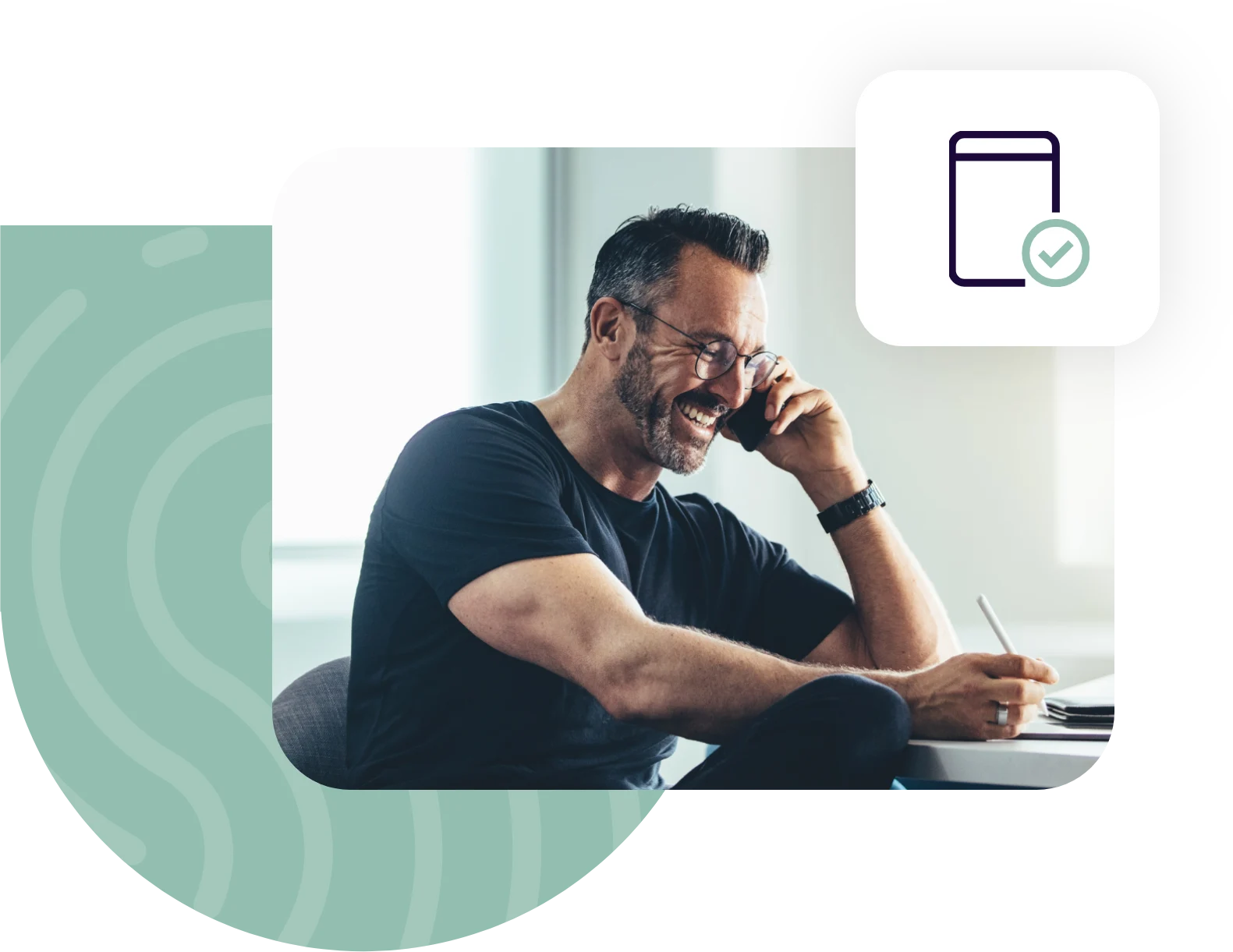

Public Key Cryptography
A decentralized identifier along with the cryptographic public-private key pair constitute the identity wallet. Personal information about the user and their credentials are stored within the wallet and require the user’s private key and biometrics to read data from the wallet. Since the private key never leaves the Secure Enclave (ie, Trusted Platform Module) of the device and the biometric can be authenticated to the highest digital standards available, this approach vastly exceeds the security achievable via passwords, traditional multi-factor authentication and unverified device-level biometrics. This reduces cyber threats related to account credential compromise such as phishing, data breach and compromised account credentials.
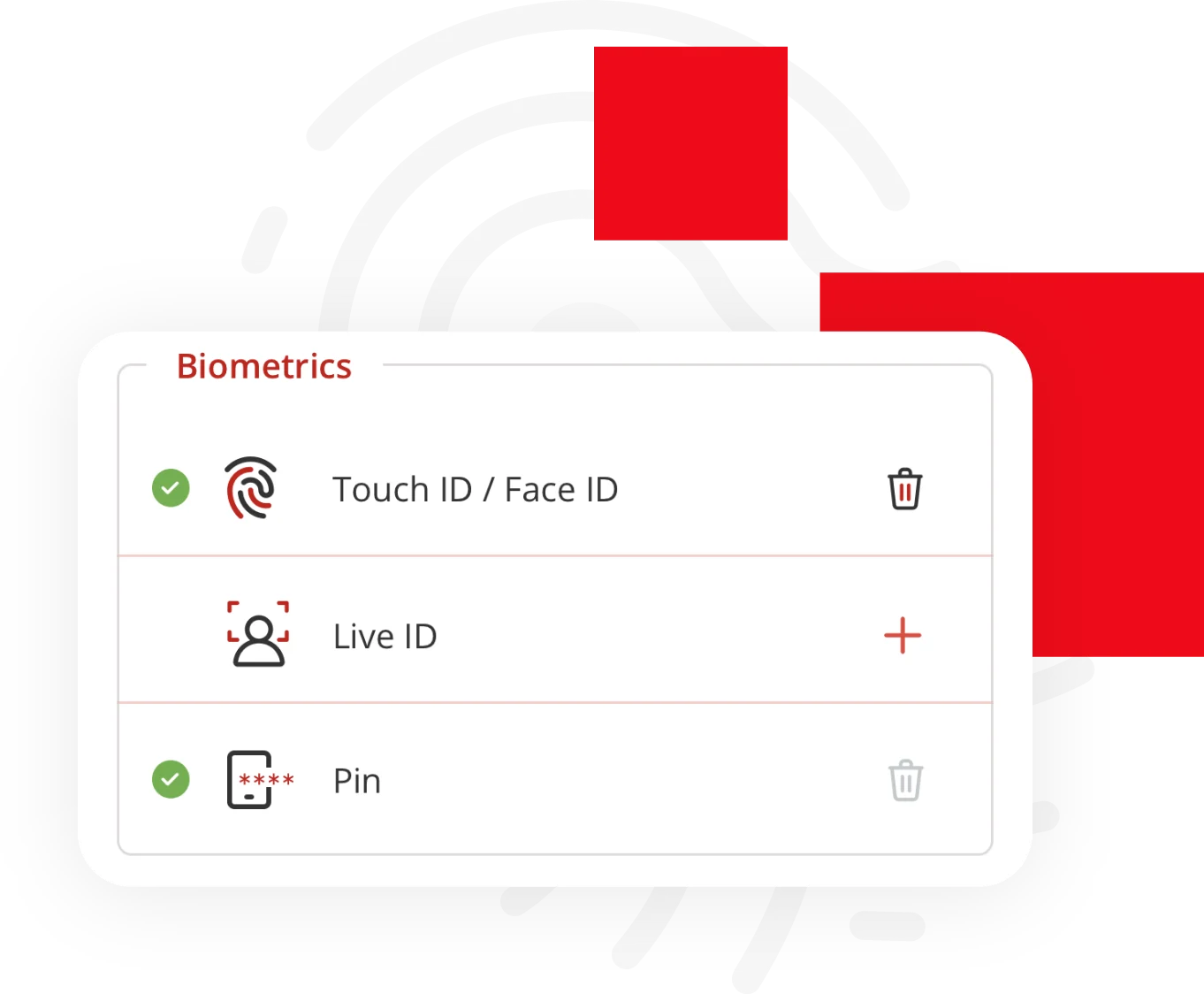
User Convenience
When data from the digital wallet needs to be presented, for example during login or for step up authentication, the wallet holder needs to present their biometrics and consent to share data. When approved, the private key is presented as a credential to unlock the wallet and share data. The private key never leaves the device and hence it is minimized from compromise. There are no passwords to remember or clumsy codes that need to be entered.
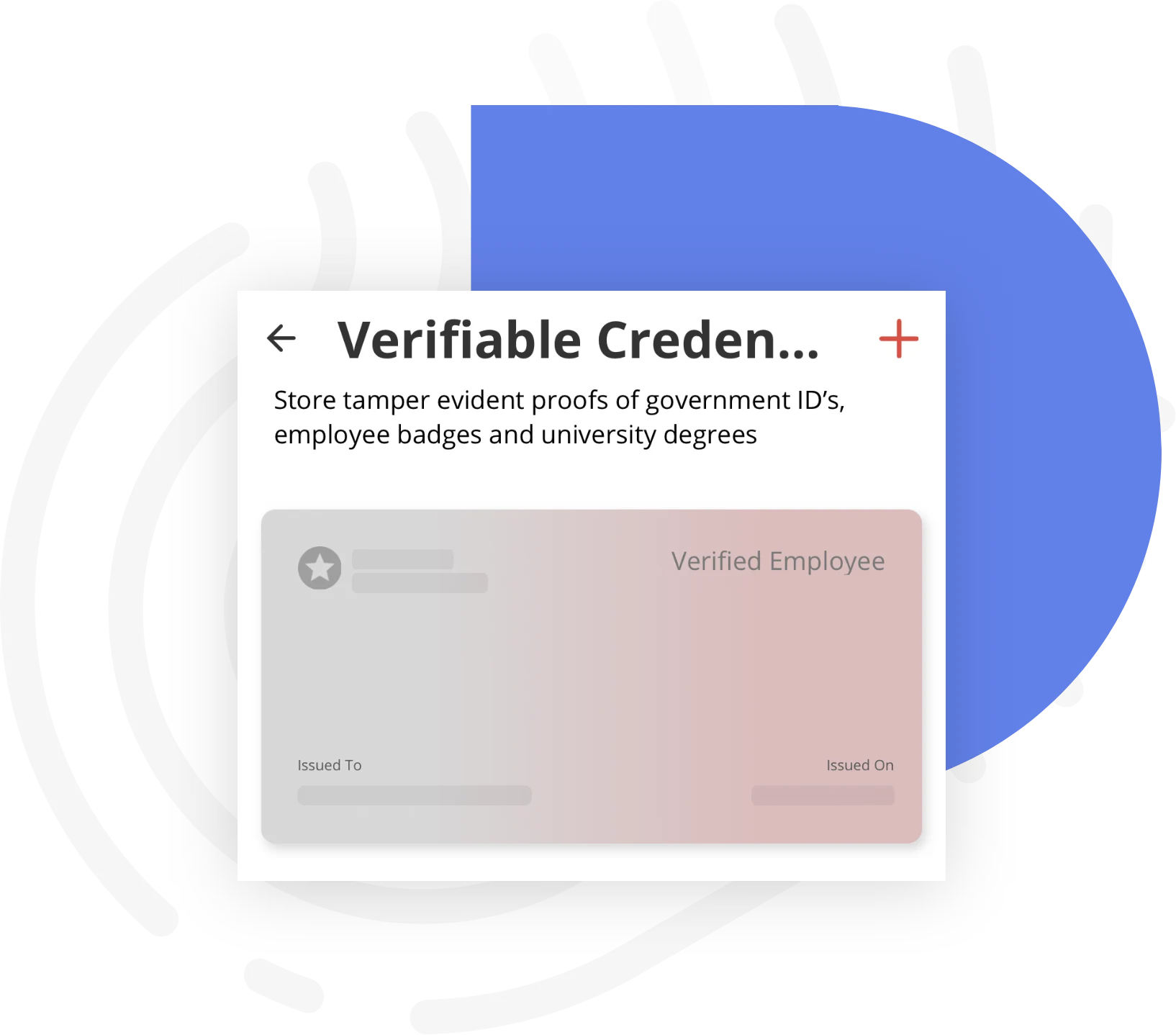
Verifiable Credentials
Verifiable credentials are a standardized method for issuing and presenting claims about a person’s identity (e.g., driver’s license, university qualifications, passport, gym membership, etc.) online. Other types of information such as educational certificates and vaccination records, for example, can also be added to the identity wallet to make the user’s ID proofing process indisputable to support a variety of use cases. An identity wallet can make assertions (without revealing the data itself) which are cryptographically verifiable by the receiving party. The major cryptographic element used by decentralized identities to request and validate verifiable credential assertions is known as a zero knowledge proof (ZKP). Zero knowledge proof satisfies an information request while protecting user privacy.